Electric cars are becoming increasingly popular. Indeed, they are being sold as being essential to our future and to our planet. But do they really make a difference compared with conventional cars? Are they really the future?

“Electric cars are cheaper to run, but they are no cheaper to make, especially in terms of the batteries, which require lithium and are much bigger than a normal car,” explains Théo Rousselin, a salesman at Autodistribution in Grasse. From 2035, new combustion-powered cars will no longer be sold on the European market, and electric cars will take their place. This decision was taken by the members of the European Union in March 2023. The reason? It’s because they’re more environmentally friendly, and will act as a bulwark against global warming, which is getting worse all the time. In France alone, transport accounts for 30% of CO2 emissions.
Electric cars have been invading the market since the end of the 20th century. There are several types: “Hybrid vehicles are powered by a combustion engine and a hybrid electric motor. Rechargeable hybrids work in the same way, except that when the car is on the internal combustion engine, the hybrid motor is recharged by the internal combustion engine. And finally, there’s the full electric, which means there’s no combustion engine,” explains Théo. Every car is different. The size of the battery, for example, varies from model to model.
Petrol or electric?
But is it better to drive electric or petrol? We tend to think that electricity is always cheaper than petrol. But this depends on the local electricity tariff, the battery capacity, the type of charger used and also the price of fuel at the pump. If we take Nice as an example, on average 1 kWH costs €0.20. Conversely, 1 litre of petrol costs €1.8. If I want to recharge the battery of my electric car, which has a capacity of 40 kWh, to the maximum, I’ll have to pay €8. If I want to fill up my car with petrol, which has a capacity of 40 litres, I’d have to spend €72.
There’s no doubt that an electric car is more cost-effective than a conventional car in the long term, especially in France. Yes, petrol is relatively expensive in France. On the other hand, France has a large number of nuclear power stations and is not dependent on a shortage of electricity.

And its manufacture?
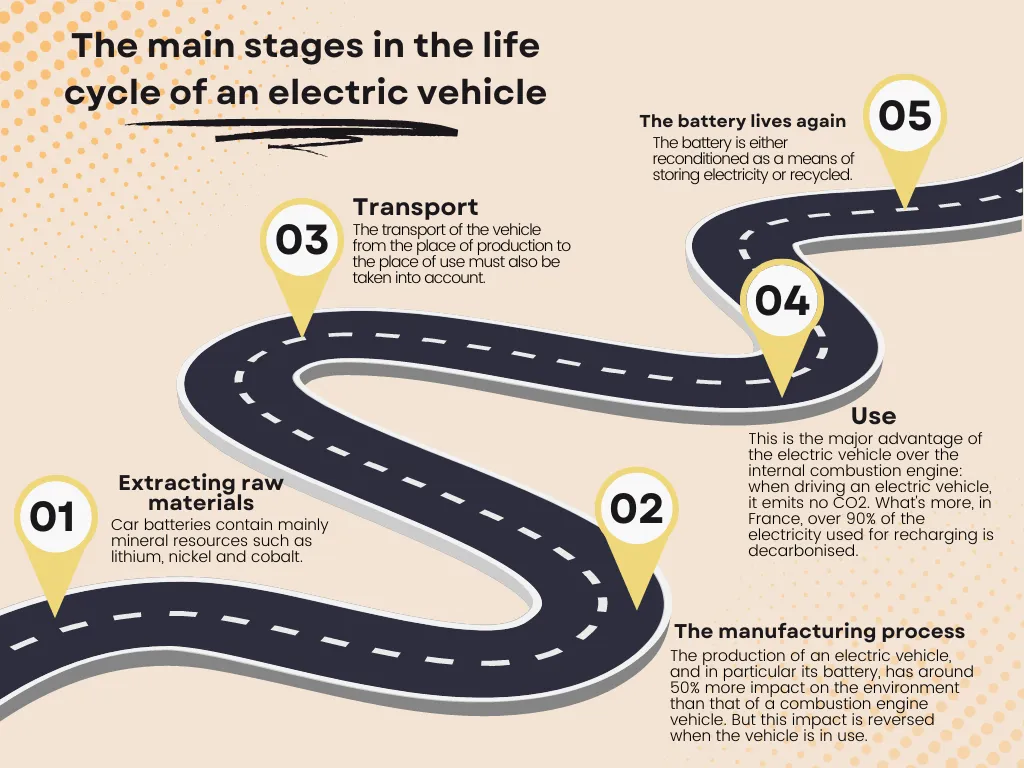
For this type of car, it is the manufacture of the battery that causes the most pollution, as it can lead to greenhouse gas emissions. However, over time, advances in technology have helped to reduce these emissions. The most expensive ingredient? Lithium. Lithium enables cars to recharge more quickly, last longer and provide greater energy density. But it’s a highly flammable and dangerous product: “Lithium is a dangerous product, but it’s highly regulated. The batteries are protected in thermal containers and cannot heat up”, Théo assures us. According to a study by Pricewaterhouse Coopers, the production of electric vehicles currently costs manufacturers around €4,500 more than a combustion model. By comparison, a rechargeable hybrid would cost €3,600 more.
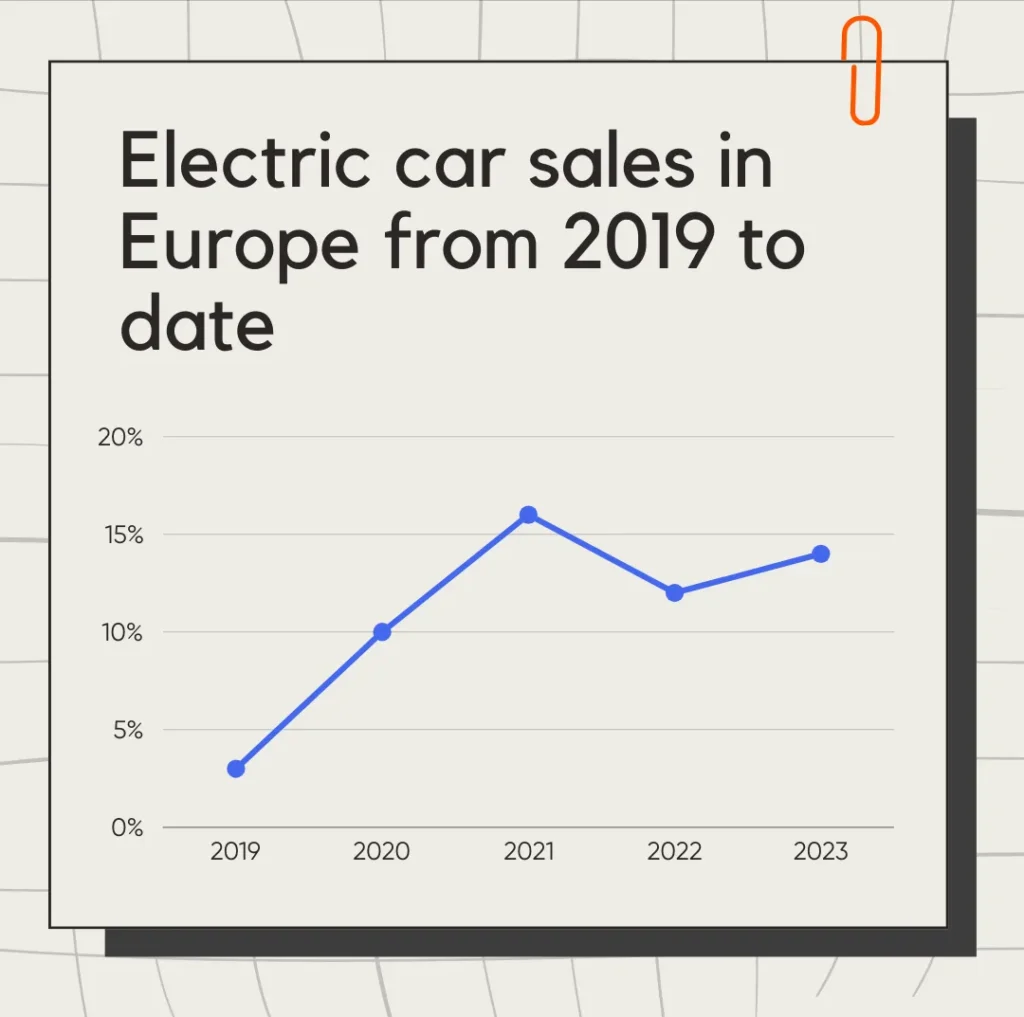
On the whole, electric cars are more cost-effective and environmentally friendly than conventional cars, even if some people are rather reluctant to use them. Nonetheless, they will have to think about it, because the UN seems determined to impose them. Europe is the world’s biggest market for electric cars, ahead of China, and is determined to make electric cars the future. The acceleration in sales has pushed up the market share of the main European countries by 25%. Since May 2023 alone, no fewer than 1,000,000 charging points have been installed on French soil. But they may have to be abandoned in favor of a growing innovation: the wireless battery.


